 Waterstop Belt: Waterstop Belt:
Introduction of waterstops: Concrete structures are only as watertight as the waterstops that join them. Structures such as water treatment plants, reservoirs, locks, dams, and below grade facilities, most likely have a waterstop system in place. Several factors must be considered when selecting a waterstop. They include, but are not limited to, joint type and joint movement, hydrostatic pressure and chemical exposure.Mechanical waterstops are embedded across and along the joint to create a diaphragm. Many profiles are suitable for moving joints: PVC, Rubber, Stainless Steel. Common Rubber    |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
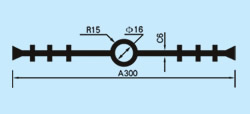
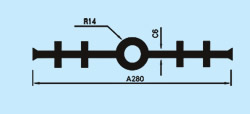
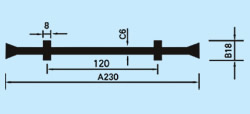
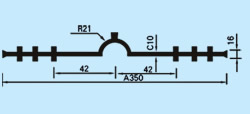
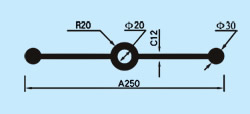
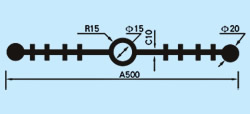
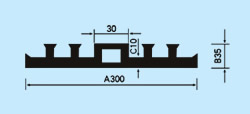
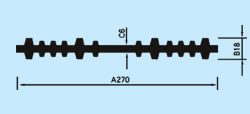
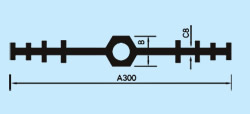
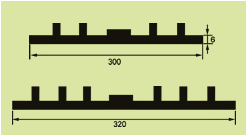
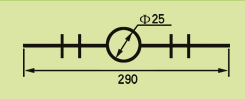
| Description: Rubber water stop belt utilizes high elasticity and compressibility of rubber to deform its elastomer body under various kinds of loads to fasten and seal, prevent building's leakage and seepage effectively. And it can act as buffer to absorb shock. Because of discontinuous construction and foundation distortion, there have to be some construction gap, subsidence gap and distortion gap etc in many project constructions. Therefore the water stop belt must be applied in these gaps against water leakage problems. Cross section view of waterstop belts: |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Site Map | ||
 |
|
|
|
|
||
 |
|
||||||||||||||||||
 |
Copyright © 2008-2009 • Anber Machine(Hebei) Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
Tel: 0086-510-88239310/88239309; Fax: 0086-510-88237950 Email: lixiaoyan@china-anbermachine.com; sales@expansion-joint-china.com |
||||||||||||||||||